What Is The Average Annual Growth Rate (AAGR)?
The Average Annual Growth Rate (AAGR) is a commonly used metric to measure the average growth of a quantity over a specified period of time. It is particularly useful in financial analysis, business planning, and investment evaluation.
Formula
The formula for calculating Average Annual Growth Rate (AAGR) is:
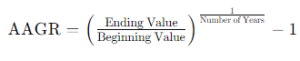
Where:
- Ending Value: The value of the quantity at the end of the period.
- Beginning Value: The value of the quantity at the beginning of the period.
- Number of Years: The number of years over which the growth occurred.
Calculation
Let’s say you want to calculate the AAGR of a company’s revenue over a 5-year period:
- Beginning Value (Revenue at the start of the period): ₹1,000,000
- Ending Value (Revenue at the end of the period): ₹1,800,000
- Number of Years: 5 years
AAGR=(1800,000/1,000,000)1/5 −1
AAGR=(1.8)0.2−1
AAGR=1.1487−1
AAGR=0.1487
AAGR≈14.87%
In this example, the Average Annual Growth Rate (AAGR) of the company’s revenue over the 5-year period is approximately 14.87%. This means that, on average, the company’s revenue grew by about 14.87% each year over the specified period.
Interpretation Of AAGR
The Average Annual Growth Rate (AAGR) is a valuable metric used to understand the average rate at which a quantity (such as revenue, profit, investments, etc.) has grown over a specific period of time. Here’s how to interpret AAGR effectively:
- Rate of Growth: AAGR indicates the average percentage increase or decrease per year for the given period. For instance, an AAGR of 10% means that, on average, the quantity in question has grown by 10% per year over the specified period.
- Smoothed Growth Rate: AAGR smooths out the annual fluctuations in growth and provides a consolidated view of the overall growth trend. It helps to understand the consistent pace of growth over time rather than focusing on individual year-to-year variations.
- Comparative Analysis: AAGR allows for comparison between different entities or periods. For example, comparing the AAGR of revenue growth between two companies can reveal which company has experienced faster or more consistent growth over the same period.
- Forecasting and Projection: AAGR can be used for forecasting future performance based on historical growth trends. However, it’s important to consider other factors that may impact future growth, such as market conditions, competition, and economic factors.
- Investment Performance: In investments, AAGR is crucial for evaluating the performance of stocks, mutual funds, or portfolios. It helps investors assess the average annual return on their investments over a specified timeframe.
- Long-term Planning: Businesses use AAGR to plan long-term strategies and set realistic growth targets. It provides insights into whether current growth rates are sustainable or if adjustments are needed to achieve desired objectives.
- Risk Assessment: A declining or negative AAGR can indicate challenges or weaknesses in a business or investment. It prompts stakeholders to analyze underlying factors and take corrective actions to improve growth prospects.
- Contextual Understanding: AAGR should be interpreted in the context of the industry, economic environment, and specific circumstances affecting the entity in question. A high AAGR may be impressive, but it needs to be sustainable and aligned with broader market dynamics.
Applications Of AAGR
The Average Annual Growth Rate (AAGR) finds various applications across different fields, particularly in finance, economics, business analysis, and investment evaluation. Here are some key applications of AAGR:
- Financial Analysis:
- Revenue and Profit Growth: AAGR is commonly used to analyze the average annual growth of a company’s revenue or profit over a specific period. It helps in assessing the company’s performance and trend in generating income.
- Asset Growth: AAGR can be applied to assess the growth rate of assets, such as total assets, net worth, or portfolio value, providing insights into the asset accumulation rate.
- Investment Evaluation:
- Investment Returns: AAGR is crucial for evaluating the average annual return on investments, such as stocks, mutual funds, or portfolios. It helps investors compare the performance of different investments over the same period.
- Portfolio Management: Portfolio managers use AAGR to measure the growth rate of their investment portfolios, assisting in strategic asset allocation and performance benchmarking.
- Business Planning:
- Strategic Planning: Businesses utilize AAGR to set growth targets and formulate strategic plans based on historical growth trends. It aids in forecasting future performance and aligning business strategies with growth objectives.
- Market Expansion: AAGR helps businesses assess market expansion opportunities by understanding historical growth rates in new markets or product lines.
- Economic Analysis:
- Sector Analysis: Economists and analysts use AAGR to analyze the growth rates of economic sectors or industries, providing insights into sectoral performance and trends.
- GDP Growth: AAGR can be applied to measure the average annual growth rate of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) or other macroeconomic indicators, facilitating economic policy analysis.
- Forecasting and Projections:
- Future Growth Estimation: AAGR serves as a basis for forecasting future growth trends based on historical data. It assists in predicting future revenues, profits, or market demand.
- Risk Assessment: Forecasting with AAGR helps in assessing business or investment risks by identifying potential growth uncertainties or downturns.
- Performance Comparison:
- Benchmarking: AAGR allows for the comparison of growth rates between entities, such as comparing revenue growth between companies or investment returns between funds. It helps in identifying leaders and laggards in performance.
- Long-term Planning and Decision Making:
- Strategic Decision Support: AAGR provides decision-makers with data-driven insights for long-term planning and decision-making processes. It informs resource allocation, investment priorities, and expansion strategies.
Limitations Of Average Annual Growth Rate
While Average Annual Growth Rate (AAGR) is a useful metric for measuring growth trends over time, it has several limitations that should be considered when interpreting and using this metric:
- Smoothing Effect: AAGR calculates the average growth rate over a period, which can obscure significant year-to-year variations in growth rates. This smoothing effect may not reflect the volatility and fluctuations experienced during the period.
- Period Dependency: AAGR heavily depends on the specific time period chosen for calculation. Different starting and ending points can yield significantly different AAGR values, potentially leading to misleading comparisons if not properly contextualized.
- Non-Linear Growth: AAGR assumes a constant growth rate over the entire period, which may not accurately represent situations of non-linear growth. Rapid growth followed by stagnation or decline can distort the AAGR calculation.
- Doesn’t Account for Timing of Growth: AAGR treats growth as evenly distributed over each year, regardless of when growth occurred within the year. This may not capture the timing of seasonal or cyclical fluctuations that impact growth patterns.
- Sensitive to Outliers: A single exceptionally high or low growth rate in one year can disproportionately impact the AAGR calculation, potentially skewing the average and not reflecting the underlying growth trend accurately.
- Lack of Contextual Information: AAGR alone may not provide sufficient context about the factors influencing growth, such as market conditions, economic cycles, competitive dynamics, or strategic initiatives. Additional qualitative analysis is often needed to interpret AAGR effectively.
- Limited Predictive Power: While AAGR is useful for historical analysis and trend identification, it may not reliably predict future growth rates, especially in dynamic or rapidly changing environments where past performance may not indicate future outcomes.
- Different Time Frames: AAGR can produce different results depending on the time frame chosen (e.g., short-term vs. long-term AAGR). The interpretation and implications can vary, requiring careful consideration of the specific context and objectives.
- Limited Comparability: Comparing AAGR across different entities or sectors may be challenging due to varying base sizes, market conditions, and growth dynamics. Adjustments or additional metrics may be necessary for meaningful comparisons.
- Risk of Misinterpretation: Misinterpreting AAGR as a comprehensive measure of growth without considering its limitations can lead to erroneous conclusions or decisions. It should be used in conjunction with other metrics and qualitative insights for robust analysis.
Average Annual Vs. Compound Annual Growth Rate
Key Differences:
- Compounding Effect: CAGR incorporates the compounding effect of growth over time, reflecting the actual growth rate that would result in the final value. AAGR does not consider compounding and simply averages annual growth rates.
- Interpretation: CAGR provides a more accurate representation of long-term growth rates, especially for investments or assets that experience compounding effects. AAGR, on the other hand, provides a basic average growth rate without considering compounding.
- Context: CAGR is particularly useful when evaluating investments or assets that experience varying annual growth rates but benefit from reinvestment of profits. AAGR is more straightforward and may be sufficient for assessing linear growth trends.
Though both AAGR and CAGR measure growth rates over time, CAGR is generally preferred for investments and financial analysis due to its consideration of compounding effects, providing a more accurate annualized growth rate. AAGR is simpler and suitable for basic growth rate analysis where compounding effects are not a factor.
Conclusion
AAGR is a versatile tool that provides a standardized method for measuring growth rates over time, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions, assess performance trends, and plan effectively for the future. Its applications span across industries and disciplines, offering valuable insights into economic, financial, and business dynamics.