With the highly anticipated Union Budget 2025 around the corner, expectations are mounting for significant policy announcements that will steer India’s economic future. Important topics including GDP growth in 2025, tax reforms in 2025, and economic revival are anticipated to be covered by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman. The budget is also anticipated to prioritize sustainable development, affordable housing, infrastructure investment, and tax reduction in 2025. The budget for this year promises to promote strong growth and guarantee a better, more prosperous future for the nation.

Tax Reforms 2025:
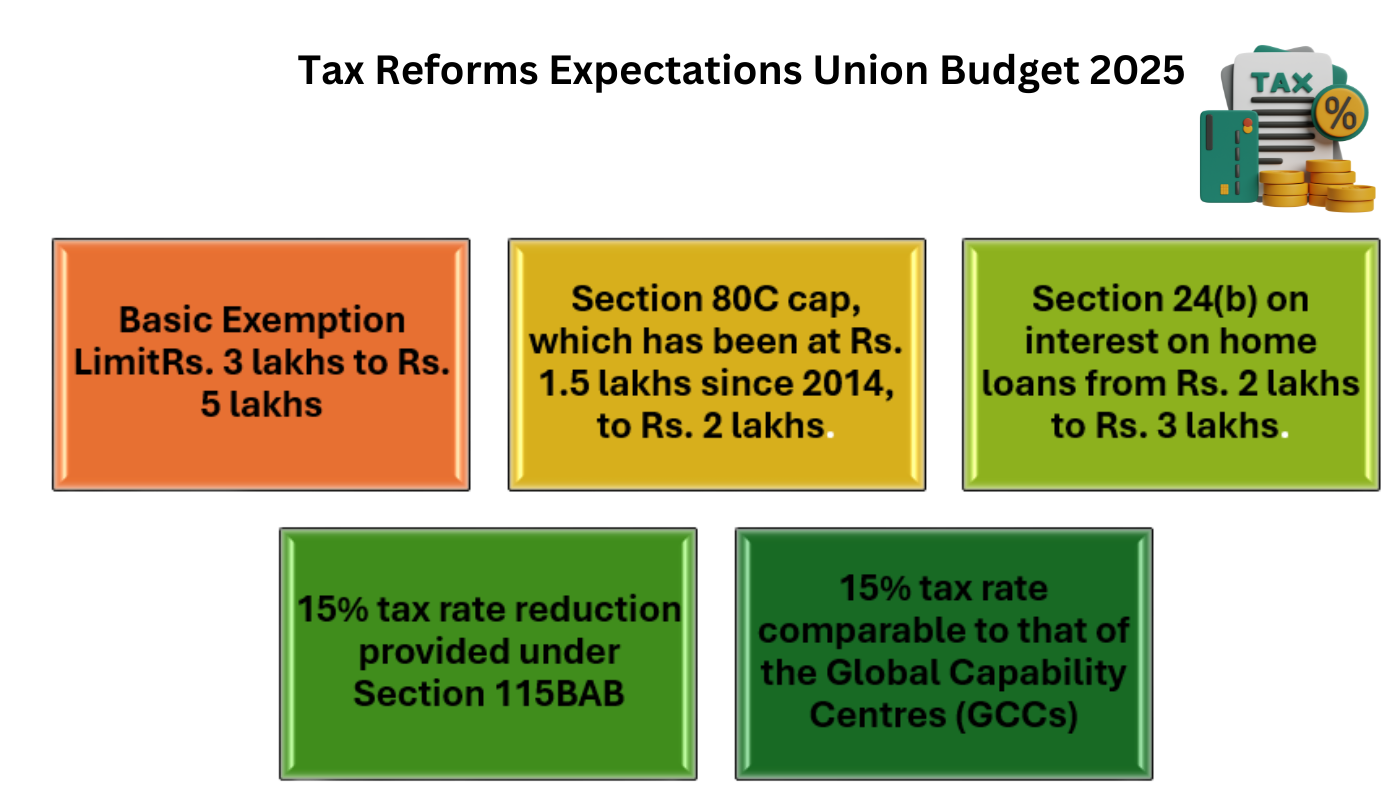
- Significant changes in tax policies are anticipated, particularly around income tax. This could include changes in tax slabs and rates to provide relief to taxpayers.
- A higher basic exemption limit could be introduced, making the tax system more progressive. Additionally, reforms are expected to simplify tax compliance and administration, enhancing ease of doing business.
- The basic exemption limit under the new regime is expected to increase from 3 lakhs to Rs. 5 lakhs, giving relief to individual taxpayers and boosting consumption and disposable income.
- The government is anticipated to raise the Section 80C cap, which has been at Rs. 1.5 lakhs since 2014, to Rs. 2 lakhs.
- To encourage homeownership and support the expansion of the real estate industry, the government may raise the deduction limit under section 24(b) on interest on home loans from Rs. 2 lakhs to Rs. 3 lakhs.
- One of the main factors luring investors to India has been the 15% tax rate reduction provided under Section 115BAB for new domestic manufacturing firms.
- Extending this rate for businesses that begin operations after April 1, 2024, would continue to spur growth as it expired in March 2024.
- Furthermore, a suggestion has been made to provide a 15% tax rate comparable to that of the Global Capability Centres (GCCs), which currently number 1,700 and are expanding, in order to support their growth and job creation.
- The government may implement new production-linked incentives for research and development (R&D) endeavours in order to promote innovation.
- These can include extra deductions for particular R&D expenses in accordance with predetermined standards, like higher capital investment, employment creation, or turnover.
Standard Deduction Increase:
In the present tax regime, the standard deduction is a flat amount deducted from the income of salaried individuals to ease their tax liability. It’s currently set at:
- ₹75,000 under the new tax regime
- ₹50,000 under the old tax regime.
- There is a growing expectation that the standard deduction limit will be increased to ₹1 lakh under both the new and old regimes.
- This increment aims to provide significant tax relief and increase disposable income for salaried taxpayers. With an increased standard deduction, taxpayers could see a reduction in their taxable income, leading to lower tax liabilities.
- This essentially translates to more money in the hands of the working population. The standard deduction does not require any proof or documentation, making it a hassle-free perk.
- An increase would further simplify the tax filing process for a larger segment of taxpayers. Higher disposable income means more spending power, potentially leading to increased consumer spending and a positive impact on the economy.
- The last increment in standard deduction was from ₹50,000 to ₹75,000 in 2024, which provided savings of up to ₹17,500 per year. Despite this relief, the cost of living continued to rise, prompting calls for further adjustment.
- The expected increase to ₹1 lakh is seen as a necessary measure to support the middle class in managing daily expenses amidst inflationary pressure.
Boost to Capital Expenditure.
- Capital expenditure (Capex) refers to the funds used by the government to acquire or upgrade physical assets such as infrastructure, buildings, and equipment. This spending is essential for creating future benefits and is a key component in stimulating economic growth.
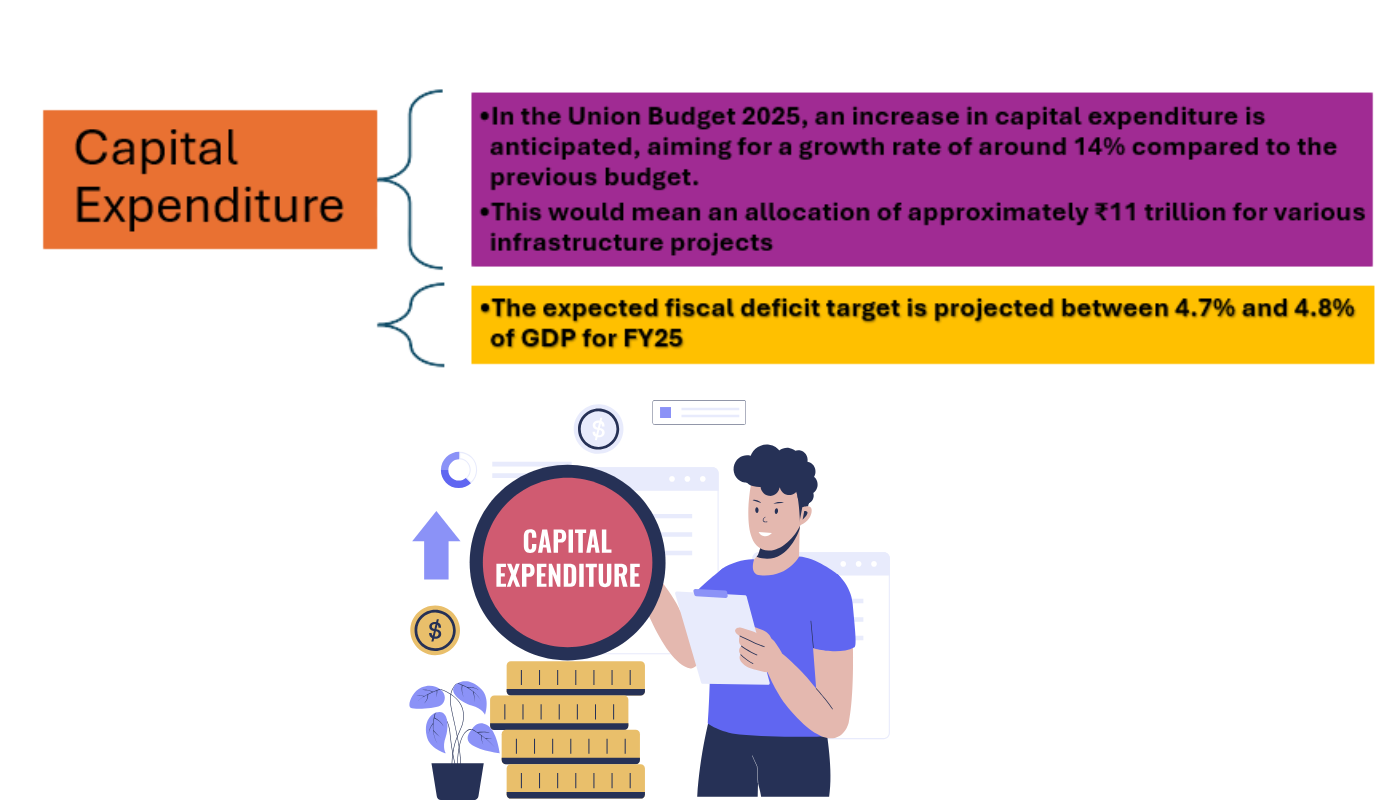
- In the Union Budget 2025, an increase in capital expenditure is anticipated, aiming for a growth rate of around 14% compared to the previous budget. This would mean an allocation of approximately ₹11 trillion for various infrastructure projects.
- Significant investments are expected in the transportation sector, covering roads, railways, airports, and ports to improve connectivity and reduce logistics costs.
- Focus on developing smart cities, enhancing urban infrastructure, and improving public amenities will be a priority.
- Projects related to water supply and sanitation will receive funding to ensure access to clean water and improved sanitation facilities in urban and rural areas.
- Increased capital expenditure is expected to generate employment opportunities, particularly in the construction and infrastructure sectors.
- By improving infrastructure, the government aims to enhance the overall productivity and efficiency of the economy, leading to sustained economic growth. Better infrastructure can attract private investments, both domestic and foreign, boosting economic activities and contributing to GDP growth. Balancing increased capital expenditure with fiscal discipline is essential. The expected fiscal deficit target is projected between 4.7% and 4.8% of GDP for FY25
Agricultural Sector Support:
- The agricultural sector is a critical pillar of India’s economy, supporting a significant portion of the population and contributing substantially to the GDP.
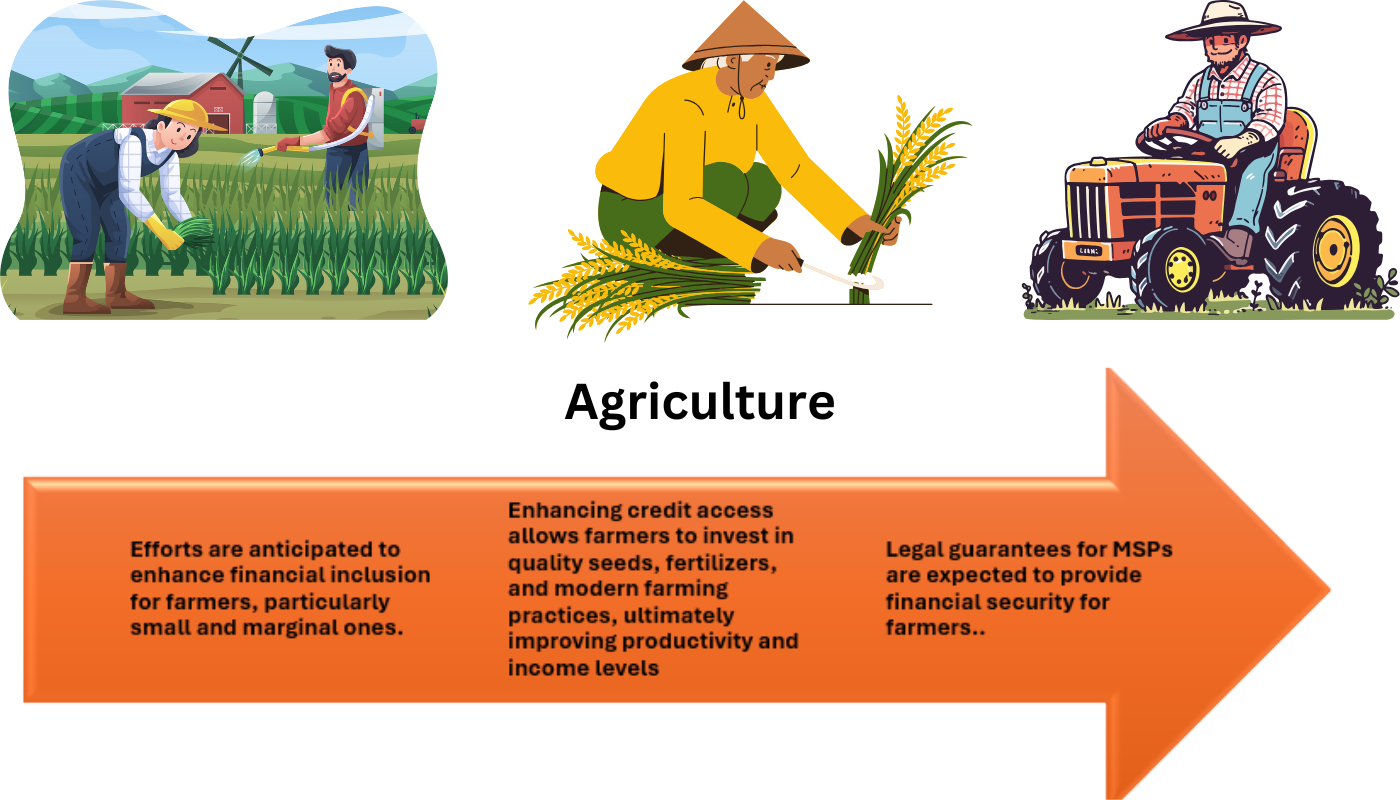
- Efforts are anticipated to enhance financial inclusion for farmers, particularly small and marginal ones.
- Agricultural credit disbursements are expected to increase, with a focus on innovative financing models to make credit more accessible and affordable.
- Enhancing credit access allows farmers to invest in quality seeds, fertilizers, and modern farming practices, ultimately improving productivity and income levels
- Upgraded irrigation systems to ensure efficient water use, addressing the scarcity of water in many regions Expanded and improved cold storage facilities to minimize wastage of perishable goods Better rural road networks to facilitate easier transportation of goods from farms to markets. Adoption of digital tools and technologies to enhance productivity, transparency, and market access for farmers.
- Legal guarantees for MSPs are expected to provide financial security for farmers. Ensuring that farmers receive a fair price for their produce, even during market fluctuations, helps in recovering production costs and reduces distress selling.
- The government aims to support and empower women in agriculture. Increased credit access and leadership opportunities for women farmers and entrepreneurs will contribute to rural economic growth and gender equality in the agricultural sector.
Sustainability and Climate Resilience
Focus on sustainable farming practices to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Micro-Irrigation Systems: Promoting schemes like Per Drop More Crop (PDMC).
- Crop Diversification: Incentivizing the cultivation of climate-resilient crops such as millets, oilseeds, and pulses.
- Renewable Energy: Integrating solar energy installations with irrigation systems to enhance energy efficiency and reduce costs. Policy supports to boost investments in agricultural R&D. Encouraging innovations in seed technology, sustainable fertilizers, and digital agriculture to optimize yields and ensure environmental sustainability
Education Sector Reforms:
- India’s education sector is poised for transformative reforms in this Union Budget. The focus is multifaceted, ranging from enhancing digital infrastructure to broadening access to higher education. In 2024, a significant allocation of ₹1.12 lakh crore was directed towards digital learning initiatives, including virtual labs and the Digital University initiative.
- The 2025 Budget is expected to build on this foundation by increasing investments in technology integration, particularly in AI, machine learning, and data sciences.
- This will involve improving internet connectivity in rural areas and providing affordable devices to students, aiming to bridge the digital divide and ensure that students from all backgrounds have equal access to quality education.
- Additionally, there is an emphasis on updating curricula to include industry-relevant skills, particularly in emerging fields like AI, cloud computing, and data visualisation.
- Funding and policy reforms are critical. With India’s public spending on education below 3% of GDP, there is a push for increased funding to ensure the growth and accessibility of education. Stakeholders call for allocating 6% of GDP to educational initiatives, focusing on infrastructure, teacher training, and digitalization.
- Moreover, strengthening industry-academia partnerships can enhance job readiness among graduates. Initiatives such as educational loans for economically weaker students, funding for STEM research, and skill development programs are essential steps towards making education more affordable and accessible.
- Enhancing hands-on training and providing internships in real-world settings is also crucial for preparing students to enter the labour market. By fostering a globally competitive workforce, India can significantly boost its economic growth.
- The 2025 Budget is expected to focus on these key areas to build a future-ready education system that aligns with global trends and addresses the unique challenges faced by India’s diverse education ecosystem
Healthcare Investments:
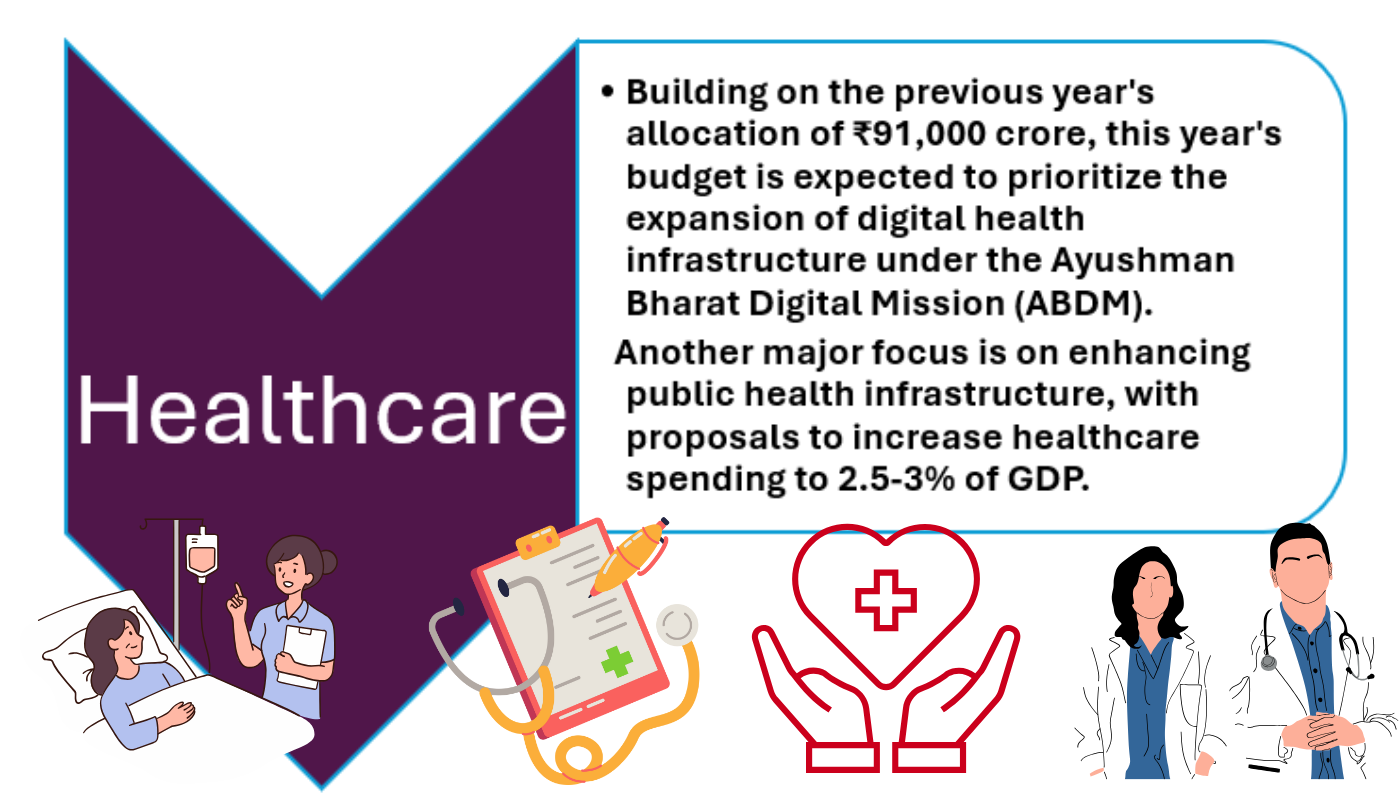
- Union Budget 2025 promises to be pivotal for India’s healthcare sector, with an emphasis on accessibility, affordability, and digital transformation. Building on the previous year’s allocation of ₹91,000 crore, this year’s budget is expected to prioritize the expansion of digital health infrastructure under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
- Significant investments in telemedicine services, AI-driven diagnostics, and electronic health records (EHRs) are anticipated. These measures aim to bridge the urban-rural healthcare divide, ensuring that remote communities have access to quality healthcare services. Another major focus is on enhancing public health infrastructure, with proposals to increase healthcare spending to 2.5-3% of GDP.
- This includes investing in primary healthcare facilities, improving disease surveillance systems under the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission, and upgrading district hospitals.
- Affordability remains a pressing issue, as nearly 63% of medical expenses are borne out-of-pocket by patients.
- Expanding insurance coverage under Ayushman Bharat to include outpatient services and preventive care, along with rationalizing GST rates for medical devices and diagnostics, could help alleviate financial burdens. Further, the budget is expected to support domestic manufacturing of medical devices and pharmaceuticals through the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme.
7. Encouragement for Electric Vehicles (EVs):
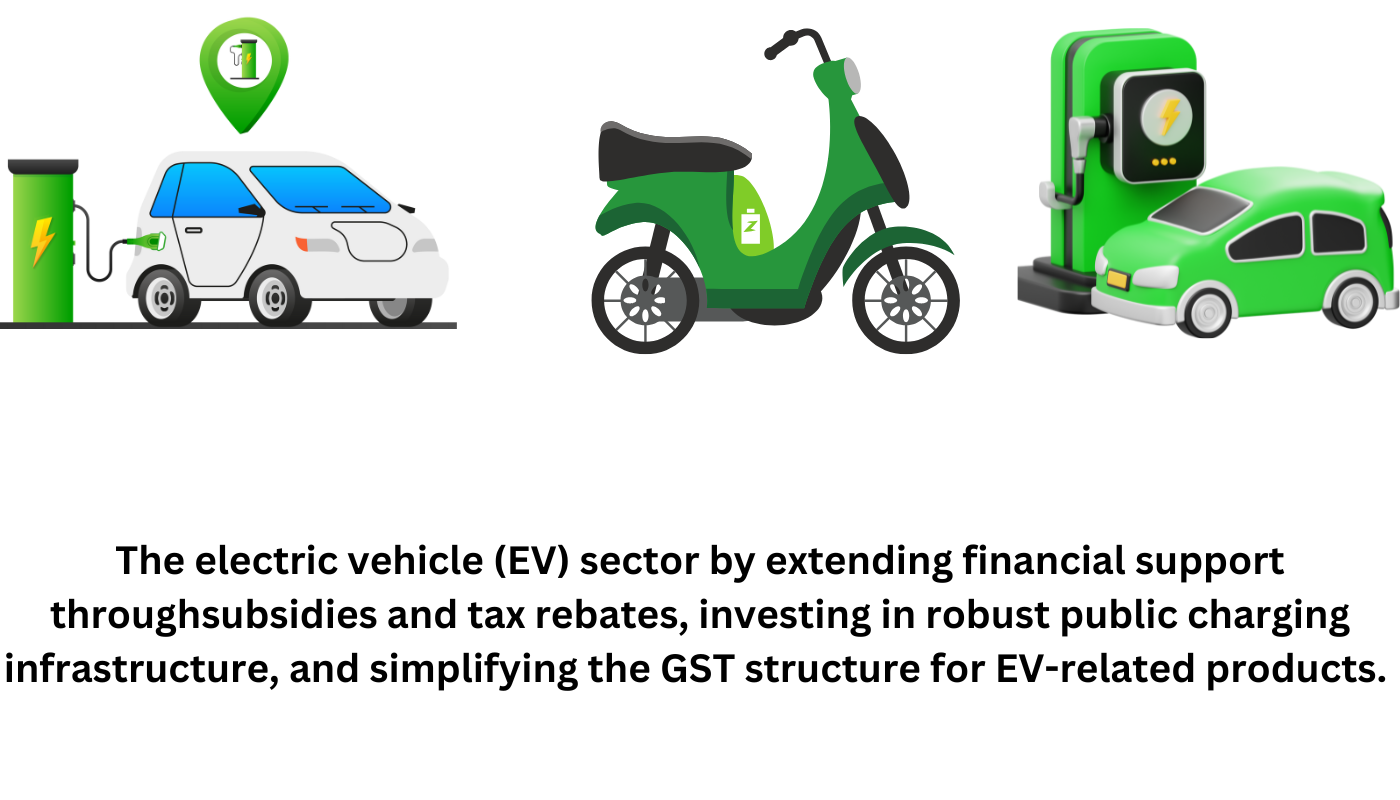
- The upcoming Union Budget 2025-26 is expected to prioritize the growth of the electric vehicle (EV) sector by extending financial support through subsidies and tax rebates, investing in robust public charging infrastructure, and simplifying the GST structure for EV-related products.
- Local battery manufacturing is anticipated to receive a boost with reduced GST rates, while targeted subsidies and reduced interest rates on EV loans aim to make EVs more affordable.
- Additionally, the budget may promote innovation through a government-backed fund for private sector R&D, ultimately supporting environmental sustainability and energy security.
8. Fiscal Consolidation:
- The Union Budget 2025-26 is expected to prioritize fiscal consolidation by adhering to the government’s target of reducing the fiscal deficit to 4.5% of GDP by FY26.
- This involves maintaining a balance between reducing public debt and continuing to support economic growth through investments in infrastructure.
- The government aims to achieve fiscal consolidation without sacrificing growth objectives, which means measures such as moderated income tax cuts and controlled public spending will be critical.
- There will likely be a focused approach on enhancing tax efficiency, managing debt prudently, and fostering a stable economic environment for sustained growth
9. Incentives for Start-ups and MSMEs:
- The Union Budget 2025-26 is anticipated to bring significant focus on start-ups and MSMEs by offering tax reliefs, enhanced credit access, and lowered compliance burdens.
- Proposals include simplified GST structures, reduced tax rates, and subsidies tailored for these ventures to stimulate growth.
- The government is also expected to introduce measures for better access to working capital, such as streamlined loan approval processes and increased limits for credit guarantee schemes.
- Additionally, incentives might be provided for technology adoption to boost operational efficiency and market reach. These efforts aim to foster a thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem and support India’s economic ambitions.
10. Focus on Sustainability:
- The Union Budget 2025-26 emphasizes sustainability by focusing on renewable energy investments, green technologies, and eco-friendly infrastructure.
- Expected measures include subsidies for clean energy projects, incentives for adopting sustainable farming practices, and policies promoting eco-friendly transportation like electric vehicles.
- There will likely be increased funding for research in green technologies and initiatives to lower the carbon footprint across industries. These steps aim to balance economic growth with environmental responsibility and ensure long-term sustainability.
Conclusion
- Thus In 2025, India’s Union Budget is anticipated to prioritize economic growth while striking a balance between fiscal discipline and sustainability. Key expectations include income tax reforms, higher capital expenditure, and support for emerging technologies.
- The agriculture sector is set to receive increased investments and subsidies. There is also a significant emphasis on innovation, upskilling, and promoting green energy initiatives.
- This comprehensive approach aims to stimulate consumption, enhance GDP growth, and foster a more inclusive economy, driving progress towards India’s ambitious growth targets