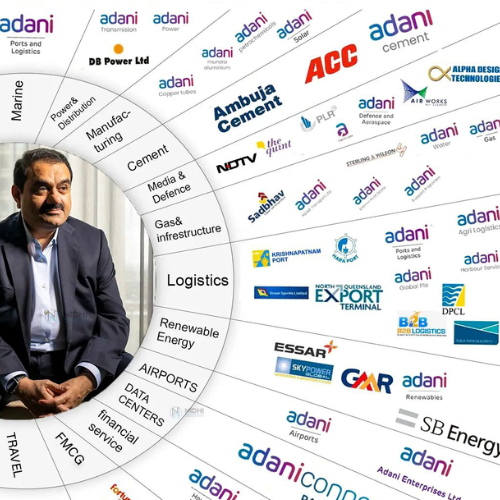
Gautam Adani -The Man who embodies the spirit of resilience and determination, inspiring countless others to pursue their dreams in the face of challenges. He is an influential Indian Industrialist and the founder and chairman of Adani Group, a globally integrated infrastructure player with businesses spanning across various sectors, including energy, resources, logistics, agribusiness, real estate, and defence. Born on June 24, 1962, in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, Adani began his career as a diamond trader before venturing into the commodities business in the late 1980s.
Under his leadership, the Adani Group has rapidly expanded, emerging as one of India’s largest conglomerates and a significant contributor to the country’s economic growth. Gautam Adani’s entrepreneurial spirit, coupled with his commitment to innovation and sustainability, Let us understand his journey in detail.
Family and Personal Life
- Gautam Adani, born on June 24, 1962, in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, hails from a modest Jain family. He grew up in a close-knit family with seven siblings, which instilled in him a sense of resilience and entrepreneurship from an early age. While he initially pursued college education in commerce at Gujarat University, he soon left to follow his passion for business and started working as a diamond sorter in Mumbai before establishing his ventures.
- Gautam Adani is married to Priti Adani, a qualified dentist and philanthropist who actively leads the Adani Foundation, the charitable arm of the Adani Group. Through the foundation, Priti focuses on education, healthcare, and community welfare initiatives, including rural development programs across India.
- The couple has two sons, Karan Adani and Jeet Adani. Karan Adani holds a key position in the Adani Group as CEO of Adani Ports and SEZ Limited, contributing to the growth and expansion of the group’s infrastructure businesses. Jeet Adani is also actively involved in the family business, overseeing strategic finance and the Adani Group’s expansion in various sectors.
Business Career
1990s – Expansion into Infrastructure and Ports:
Adani’s entry into infrastructure began in the 1990s when he won the contract to develop the Mundra Port in Gujarat. This project became the foundation of Adani Ports and SEZ Limited, which went on to become India’s largest private port operator, handling a substantial portion of India’s cargo traffic.
Mundra Port’s success demonstrated Adani’s ability to develop large-scale infrastructure projects, propelling him into the spotlight.
2000s – Diversification into Power and Energy:
Adani made his foray into the power sector by establishing Adani Power Limited in 2006, focusing on coal-based power generation. With this, the Adani Group became India’s largest private sector power producer.
His ventures expanded to include coal mining in India and Indonesia, giving the Adani Group control over the supply chain from mining to transportation and distribution.
2010s – Foray into Renewable Energy:
Recognizing the importance of sustainability, Adani pivoted to renewable energy. Adani Green Energy was launched with a focus on solar and wind power, with the company now holding one of the largest solar power portfolios globally.
By entering the renewable sector, Gautam Adani positioned the Adani Group as a key player in India’s transition to clean energy, aligning with the Indian government’s goals for sustainable energy growth.
Logistics, Defence, and Aerospace:
The Adani Group expanded further into logistics, developing integrated solutions across ports, railways, and warehouses, cementing its position as a logistics leader.
In Defence, Adani established ventures in collaboration with international companies to manufacture high-tech defence equipment in India, part of the “Make in India” initiative to bolster domestic manufacturing.
Digital and Data Infrastructure:
Recently, Adani has ventured into data centres and digital infrastructure, collaborating with companies like Microsoft to develop data centres across India. This move reflects the growing demand for digital infrastructure and is part of Adani’s broader vision of creating a technology-focused ecosystem.
Rise of Adani Group
The rise of the Adani Group is a testament to Gautam Adani’s vision, risk-taking capabilities, and strategic planning. Starting from a small trading business, the group has grown into a global conglomerate with diversified interests across various sectors. Here’s an overview of the factors that fueled the meteoric rise of the Adani Group:
Early Beginnings and Foundation (1988 – 1990s):
- Gautam Adani established Adani Enterprises in 1988, initially focusing on commodity trading. The company began with exports and trading of agricultural products, coal, and other commodities, laying the groundwork for the group’s future diversification.
- In the 1990s, Gautam Adani made a strategic entry into infrastructure by bidding for the development of Mundra Port in Gujarat. Mundra would later become India’s largest private port and a major logistical gateway for the country.
Diversification into Infrastructure and Ports (1990s – 2000s):
- The Mundra Port project, completed in the late 1990s, marked a turning point. The Adani Group established Adani Ports and SEZ Limited (APSEZ), which rapidly grew to handle a significant portion of India’s cargo, making it the largest commercial port in the country.
- This venture into infrastructure allowed the Adani Group to build strong foundations, with Gautam Adani setting the stage for expansion into large-scale infrastructure and logistics.
Expansion into Energy and Power (2000s – 2010s):
- In the early 2000s, Adani entered the energy sector, recognizing the vast potential in power generation. He launched Adani Power Limited in 2006, establishing the group as India’s largest private sector power producer.
- Alongside power generation, Adani also acquired coal mines domestically and in Indonesia, enabling the group to secure its supply chain for its thermal power plants. This vertical integration helped Adani Power become a dominant player in the Indian energy landscape.
Rise in Renewable Energy (2015 – Present):
- In response to global shifts toward clean energy, Adani ventured into renewable energy through Adani Green Energy. With large-scale investments in solar and wind energy, the Adani Group became one of the largest renewable energy companies in the world.
- The group’s focus on sustainability helped it align with India’s green energy goals, earning support from international investors and partnerships. Adani’s commitment to renewable energy also contributed to the diversification of its energy portfolio.
Expansion into New Sectors: Defence, Aerospace, and Digital Infrastructure (2018 – Present):
- Adani diversified further by entering sectors such as defence and aerospace, capitalizing on India’s “Make in India” initiative to boost domestic manufacturing. Adani Defence and Aerospace collaborated with international firms to manufacture Defence equipment locally.
- The group’s recent entry into digital and data infrastructure with data centres and other digital assets underscores its vision for the digital economy’s future. Collaborations with technology giants have made Adani Group a player in India’s growing tech infrastructure market.
International Expansion and Partnerships:
- To expand globally, the Adani Group pursued strategic acquisitions and partnerships in countries like Australia, where it acquired the Carmichael coal mine. While controversial, the project solidified Adani’s position as a global player in energy resources.
- Additionally, partnerships with companies like Total Energies in renewables have boosted Adani’s global presence and credibility, especially in the green energy sector.
Vertical Integration and Self-Sufficiency:
- A major factor behind the Adani Group’s rise is its vertical integration strategy. By controlling various parts of its operations—from resource extraction to logistics and distribution—Adani has minimized dependencies on third-party suppliers, creating a resilient and efficient business model.
Government Support and Policy Alignment:
- The Adani Group’s alignment with India’s infrastructural and economic policies, including “Make in India” and renewable energy goals, has often worked in its favour, securing favourable regulatory conditions and government support.
Strategic Risk-Taking and Innovation:
- Gautam Adani’s ability to take calculated risks, such as large-scale investments in emerging sectors and geographic expansions, has set the Adani Group apart. This strategic foresight has led to early moves in high-growth sectors, keeping the company ahead of its competitors.
Strong Leadership and Vision:
- Gautam Adani’s leadership, marked by resilience and ambition, has been instrumental in the group’s growth. His hands-on approach and long-term vision have enabled the group to achieve massive scale while maintaining a strong focus on diversification and sustainability.
The Role of Innovation and Technology in Adani Business
- Adani Group has embraced digital transformation across its operations, employing data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) to streamline processes, improve decision-making, and enhance operational efficiency.
- By implementing predictive analytics, the group optimizes logistics and supply chain management, minimizing delays, reducing costs, and improving service quality.
- Through Adani Green Energy, the group has pioneered the use of advanced solar and wind technologies to support India’s renewable energy goals. They have invested in large-scale solar plants that use automated cleaning systems and AI-based power forecasting to increase efficiency and reduce water usage.
- Adani’s investments in renewable energy technology have positioned the group as a leader in green energy, helping to mitigate environmental impact while contributing to India’s clean energy targets.
- Adani Ports and SEZ Limited (APSEZ) has implemented smart port technologies such as IoT-enabled sensors, real-time monitoring systems, and automation to improve port efficiency. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, efficient cargo handling, and optimized resource management.
- The adoption of blockchain in logistics has helped enhance transparency and security in cargo tracking, leading to faster and more reliable shipping processes.
- The Adani Group uses AI-driven automation in construction, which accelerates infrastructure projects and reduces the need for manual labour. This approach has been particularly beneficial in large projects, including highways, airports, and metro rail systems.
- Digital twins and 3D modelling technologies allow the group to simulate and optimize infrastructure projects before construction begins, ensuring precision and cost-effectiveness.
- In the aerospace and defence sectors, Adani has partnered with technology leaders to manufacture and develop advanced defence systems within India. This includes integrating cutting-edge technology in areas such as drones, avionics, and radar systems to support India’s defence modernization efforts.
- Adani Defence and Aerospace employs innovations in materials science and engineering, leading to lighter, more resilient components critical for defence applications.
- Through its agribusiness initiatives, Adani has invested in precision agriculture technologies that improve crop yields, reduce water consumption, and enhance soil health. IoT-based sensors and remote monitoring systems allow for real-time data collection, helping farmers make informed decisions.
- The group has also invested in food processing technologies that extend the shelf life of agricultural products, reduce waste, and add value to produce, enabling farmers to increase their earnings.
Corporate Social Responsibility by Adani
Education:
Operates cost-free and subsidized schools, including Adani Vidya Mandir, providing quality education to children. Implements smart learning programs and adopts government schools in remote areas to enhance educational outcomes.
Healthcare:
Provides accessible healthcare through mobile health units, hospitals, clinics, and health camps. Offers support to differently-abled individuals and the elderly, aiming for holistic healthcare delivery.
Sustainable Livelihood:
Empowers communities via self-help groups, skill development training, and preservation of traditional arts. Tailors programs to benefit farmers, fishermen, cattle owners, youth, and women, enhancing their economic well-being.
Community Infrastructure:
Develops essential infrastructure like roads and water storage facilities to improve living standards and local economies. Acknowledges and addresses gaps in basic infrastructure to meet grassroots needs effectively.
Future Outlook
Expanding Renewable Energy Portfolio
- The Adani Group has set ambitious targets to become a global leader in renewable energy, aiming for 45 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030. With investments in solar, wind, and hybrid energy, the group is positioning itself as a key player in India’s green energy transition.
- Adani is likely to expand its battery storage and hydrogen projects to complement its renewable ventures, supporting India’s goals to reduce carbon emissions and dependency on coal.
Growth in Data Centres and Digital Infrastructure
- Recognizing the increasing importance of digital connectivity, the Adani Group plans to establish data centres across India to support the country’s digital economy. The group’s venture into data infrastructure is expected to capitalize on India’s growing demand for data storage and cloud services.
- With a focus on sustainable cooling technologies and energy-efficient operations, Adani’s data centres will likely align with its green energy initiatives.
Focus on Infrastructure Development
- Adani’s investments in ports, airports, and logistics continue to strengthen its position as India’s premier infrastructure provider. The group’s expansion into airport management has positioned it as one of the country’s largest airport operators, contributing to economic growth and connectivity.
- By integrating smart technologies into logistics and port operations, Adani is likely to improve efficiency, positioning its infrastructure assets to support India’s trade and export growth.
Ventures in Defence and Aerospace
- With India’s push for self-reliance in defence, Adani’s defence and aerospace ventures are expected to grow. The group has entered partnerships to manufacture military equipment, including drones and avionics, aligning with the government’s “Make in India” initiative.
- This sector presents opportunities for Adani to leverage technology and build a reputation as a trusted defence supplier, potentially capturing significant market share in India’s growing defence industry.
Expansion of Power Transmission and Distribution
- Adani Transmission Limited (ATL) is expected to expand its power transmission network to connect more regions, ensuring reliable electricity distribution. With the demand for efficient power infrastructure on the rise, ATL will likely play a key role in India’s grid modernization.
- The group may also expand its footprint in smart grid technology, optimizing the power flow and reducing transmission losses. This move aligns with its commitment to making energy distribution more sustainable and efficient.
Focus on Global Expansion
- The Adani Group’s ventures in international markets, especially in Australia and Southeast Asia, reflect its goal to become a global player. Its coal mining projects in Australia and its partnerships for renewable energy expansion could fuel further international investments.
- With a strategy to pursue growth opportunities abroad, the group is expected to bring Indian business standards to international markets while establishing a broader global presence.
Emphasis on Corporate Sustainability and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Standards
- The Adani Group has committed to net-zero emissions by 2050. Its investments in renewable energy, resource conservation, and environmentally friendly technologies reflect this priority.
- Strengthening ESG initiatives, especially in resource-heavy sectors like coal and logistics, could enhance the group’s image among global investors and ensure long-term sustainability.
Technological Advancements and Digital Transformation
- Embracing AI, IoT, and blockchain, Adani is focusing on digital transformation to increase efficiency across its businesses. Innovations in areas such as predictive maintenance, smart grids, and blockchain for supply chains are expected to strengthen its core operations.
- The adoption of digital technologies is anticipated to enhance transparency, efficiency, and resilience across the group’s infrastructure and energy assets, making it more adaptable to a dynamic market environment.
Potential Expansion into New Sectors
- The group’s recent foray into sectors like media suggests that Adani may continue exploring opportunities outside of its traditional domains, leveraging its infrastructure to diversify further.
- Given its history of successful diversification, the Adani Group could potentially venture into additional areas like fintech, electric vehicles, or green hydrogen, sectors poised for growth within India.
Conclusion
Gautam Adani’s journey underscores the power of vision, timing, and adaptation. Today, the Adani Group operates across sectors critical to India’s economy, from energy and logistics to food and defence. His influence has shaped Indian infrastructure, supported the nation’s green energy goals, and continues to leave an indelible mark on India’s industrial landscape.