- What Are Commodities
- What Is A Commodity Market
- How Does Commodities Business Work
- Risks Involved In Commodity Market
- Commodities Futures Trading
- Functioning Of Commodities Market
- Due Diligence
- Exchanges Involved In Commodity Market
- Structure Of Commodities Market
- International Commodity Exchanges
- Forward Markets Commission
- Commodities Transaction Tax
- Financialization of Commodities
- Points To Remember Before Trading In Commodities Market
- Study
- Slides
- Videos
10.1.Introduction
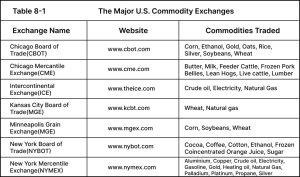
A number of commodity exchanges operate worldwide and specialize in all sorts of commodities. Although you have some overlap among some of the commodities the exchanges offer — for example gold contracts are traded on both the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) and the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) — most exchanges offer unique contracts. As such, every exchange specializes in certain commodities. For instance, the NYMEX focuses on providing investors with products to trade energy and metals; it has contracts for crude oil, propane, and heating oil as well as gold, silver, and palladium. The New York Board of Trade (NYBOT), on the other hand, focuses primarily on tropical or “soft” commodities such as coffee, cocoa, sugar, and frozen concentrated orange juice .The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) offers a wide range of products but specializes in livestock, offering contracts for live cattle, feeder cattle, lean hogs, and frozen pork bellies. Most commodities in the United States are only traded on one exchange. The feeder cattle contract is only traded on the CME, and frozen concentrated orange juice is only traded on the NYBOT. However, certain commodities are traded on more than one exchange. For example, the WTI crude oil contract is traded on both the NYMEX and the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE). In this case, you want to trade the most liquid market. You can find out where the most liquid market for a commodity is by consulting the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), which keeps information on all the exchanges and their products.
The main commodity exchanges in the United States are located in New York and Chicago, with a few other exchanges in other parts of the country.
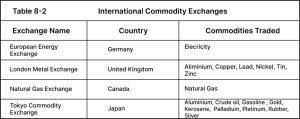
10.3. International Commodity Exchanges
The technical name for a commodity exchange is Designated Contract Market (DCM). DCM is a designation handed by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) to exchanges that offer commodity products to the public. If an exchange does not have the designation DCM, stay away from it! Commodity exchanges are responsible for setting global benchmark prices for some of the world’s most important commodities. As a result, the amount of liquidity they generate is enormous. For example, more than $1.5 Trillion worth of contracts are traded in the commodity exchanges mentioned previously — each day!
Although the bulk of commodity trading is done in the United States — the largest consumer market of commodities — there are commodity exchanges located in other countries. If you’re in the United States, you may want to consider investing in overseas exchanges for liquidity purposes. For example, aluminum futures contracts are offered on both the American NYMEX as well as the British London Metal Exchange (LME). However, the aluminum contract in the LME is more liquid, so you could get a better price by buying aluminum contracts in London as opposed to New York.